
French Impressionist Painter, Printmaker & Draftsman
1832 - 1883

Édouard Manet was a French painter. One of the first nineteenth century artists to approach modern-life subjects, he was a pivotal figure in the transition from Realism to Impressionism.
His early masterworks The Luncheon on the Grass and Olympia engendered great controversy, and served as rallying points for the young painters who would create Impressionism-today these are considered watershed paintings that mark the genesis of modern art.
Édouard Manet was born in Paris on January 23, 1832, to an affluent and well connected family. His mother, Eugénie-Desirée Fournier, was the daughter of a diplomat and the goddaughter of the Swedish crown prince, Charles Bernadotte, from whom the current Swedish monarchs are descended. His father, Auguste Manet, was a French judge who expected Édouard to pursue a career in law. His uncle, Charles Fournier, encouraged him to pursue painting and often took young Manet to the Louvre. In 1845, following the advice of his uncle, Manet enrolled in a special course of drawing where he met Antonin Proust, future Minister of Fine Arts, and a subsequent life-long friend.
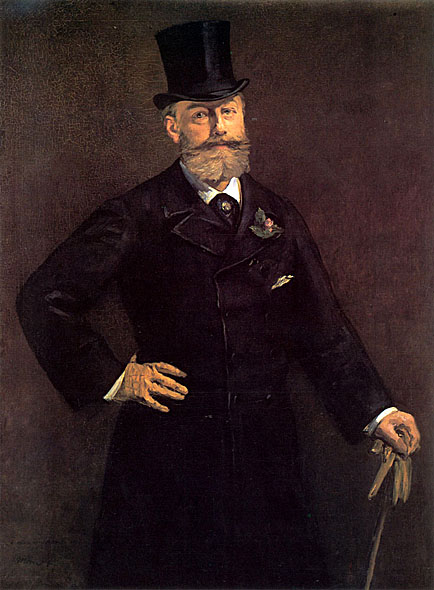


At his father's suggestion, in 1848 he sailed on a training vessel to Rio de Janeiro. After twice failing the examination to join the navy, the elder Manet relented to his son's wishes to pursue an art education. From 1850 to 1856, Manet studied under the academic painter Thomas Couture, a painter of large historical paintings. In his spare time he copied the old masters in the Louvre.
From 1853 to 1856 he visited Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands, during which time he absorbed the influences of the Dutch painter Frans Hals, and the Spanish artists Diego Velázquez and Francisco José de Goya.
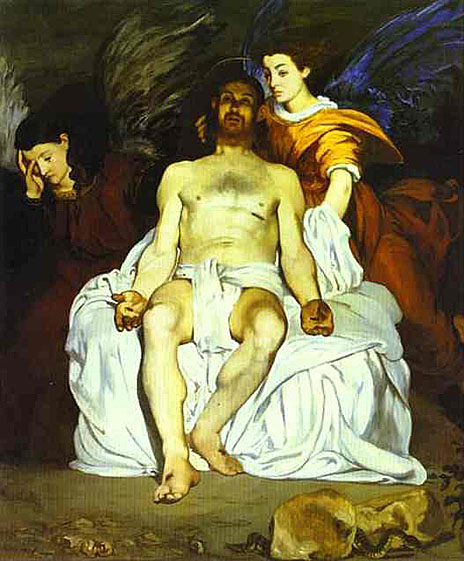
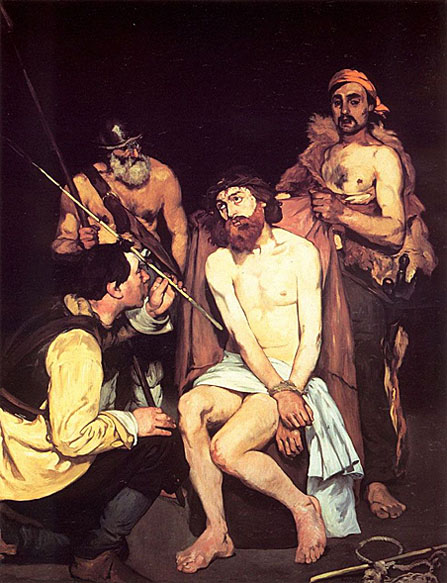
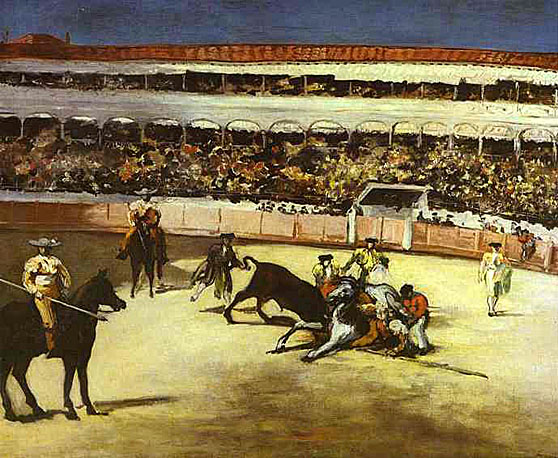
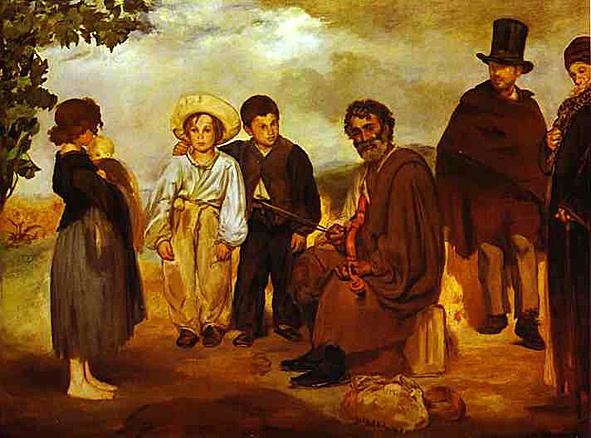
In 1856, he opened his own studio. His style in this period was characterized by loose brush strokes, simplification of details, and the suppression of transitional tones. Adopting the current style of realism initiated by Gustave Courbet, he painted The Absinthe Drinker (1858-59) and other contemporary subjects such as beggars, singers, Gypsies, people in cafés, and bullfights. After his early years, he rarely painted religious, mythological, or historical subjects; examples include his Christ Mocked, now in the Art Institute of Chicago, and Christ with Angels, in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.


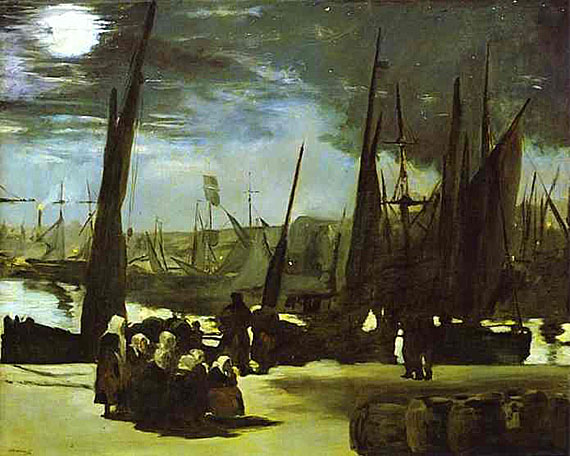
Music in the Tuileries is an early example of Manet's painting style, inspired by Hals and Velázquez, and it is a harbinger of his life-long interest in the subject of leisure. While the picture was regarded as unfinished by some the suggested atmosphere imparts a sense of what the Tuileries gardens were like at the time; one may imagine the music and conversation.
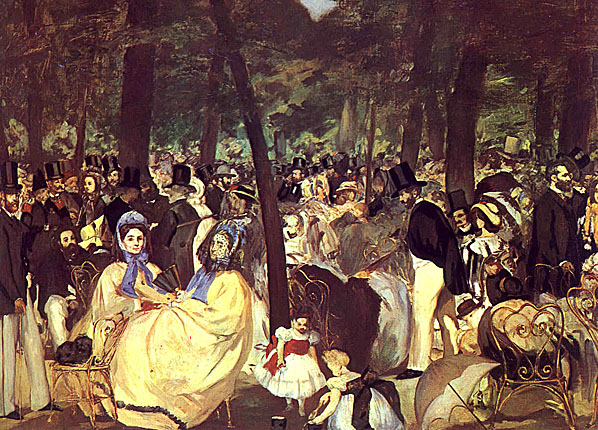

Here Manet has depicted his friends, artists, authors, and musicians who take part, and he has included a self-portrait among the subjects.
Luncheon on the Grass (Le déjeuner sur l'herbe)
A major early work is The Luncheon on the Grass (Le déjeuner sur l'herbe). The Paris Salon rejected it for exhibition in 1863, but he exhibited it at the Salon des Refusés (Salon of the rejected) later in the year. Emperor Napoleon III had initiated The Salon des Refusés, after the Paris Salon rejected more than 4,000 paintings in 1863.
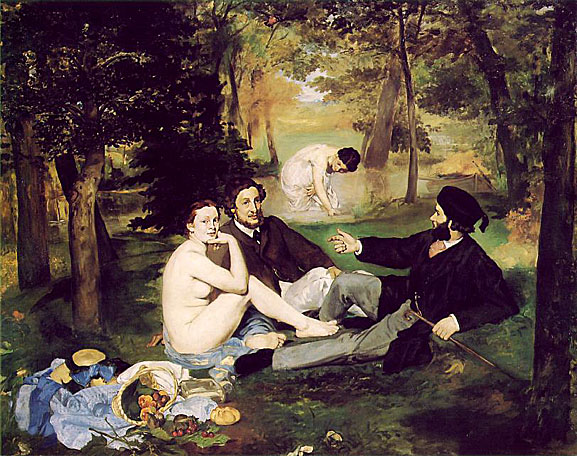

The painting's juxtaposition of fully-dressed men and a nude woman was controversial, as was its abbreviated, sketch-like handling-an innovation that distinguished Manet from Courbet. At the same time, Manet's composition reveals his study of the old masters, as the disposition of the main figures is derived from Marcantonio Raimondi's engraving of the Judgment of Paris (ca. 1515) based on a drawing by Raphael.
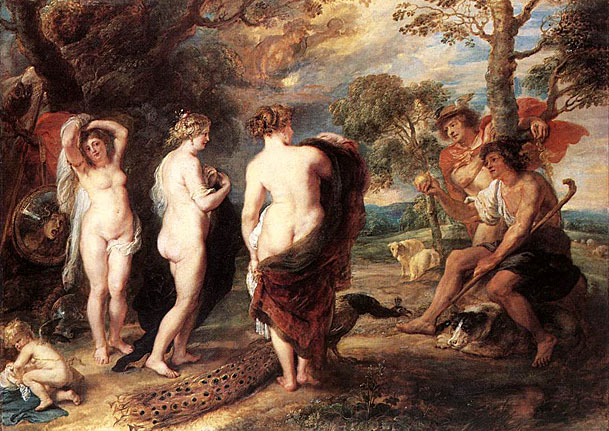
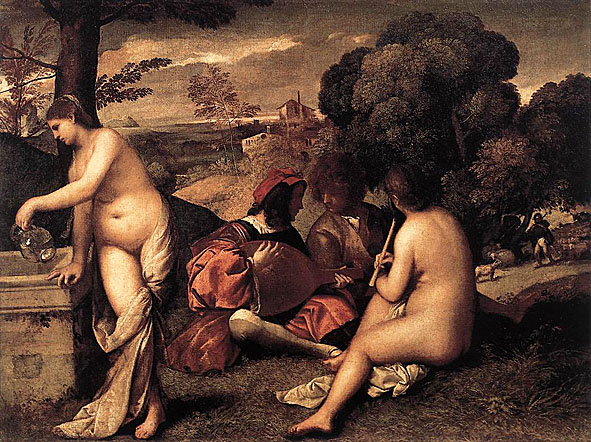
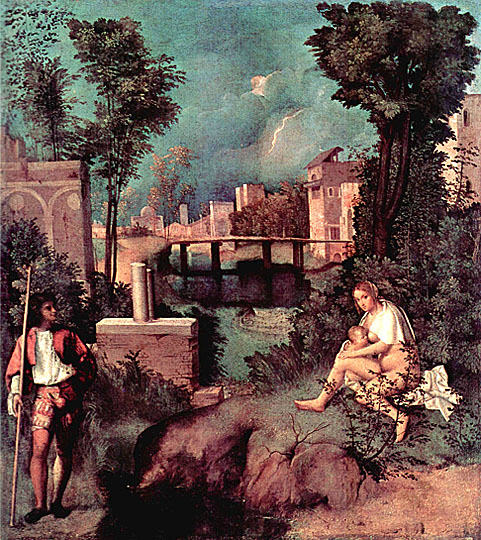
Scholars also cite two works as important precedents for Manet's painting Le déjeuner sur l'herbe, Pastoral Concert, 1508, (col. the Louvre) and The Tempest both of which are famous Renaissance paintings attributed variously to Italian masters Giorgione or Titian (circa 1508). The Tempest is housed in the Gallerie dell'Accademia of Venice, Italy. The mysterious and enigmatic painting also features a fully dressed man and a nude female in a rural setting. The man is standing to the left and gazing to the side, apparently at the woman, who is sitting in the grass, partially nude, breastfeeding a baby; darkening clouds and distant lightning herald an approaching storm. The relationship between the two figures is unclear. The painting Pastoral Concert, ca.1508 in the collection of the Louvre depicts what appears to be two seated men, both fully dressed and gazing intently at each other in a pastoral setting; the figure on the left plays a lute while the figure on the right gazes attentively at him. In the foreground two naked women accompany the two seated male figures, drapery wrapped around bare legs; one nymph has a flute, the other a pitcher of water. In the background may be seen a distant house, a copse of trees and a shepherd who appears to be playing a pipe.


Olympia
As he had in Luncheon on the Grass, Manet again paraphrased a respected work by a Renaissance artist in the painting Olympia (1863), a nude portrayed in a style reminiscent of early studio photographs, but whose pose was based on Titian's Venus of Urbino (1538). The painting is also reminiscent of Francisco Goya's painting, The Nude Maja (1800).
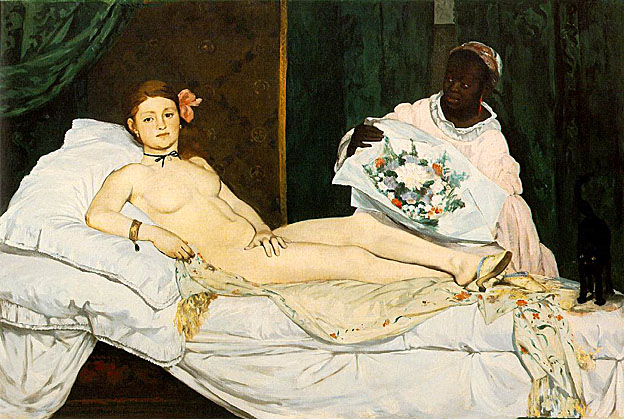
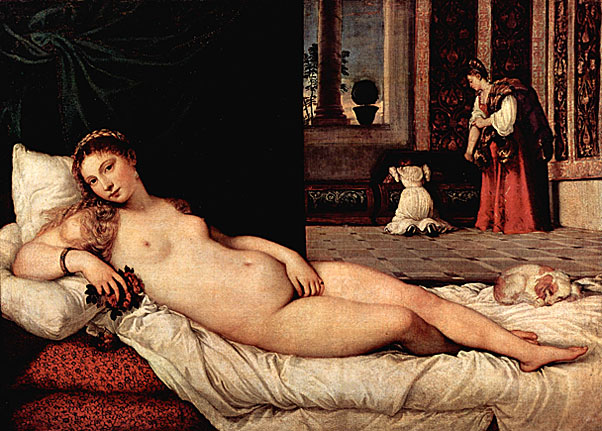

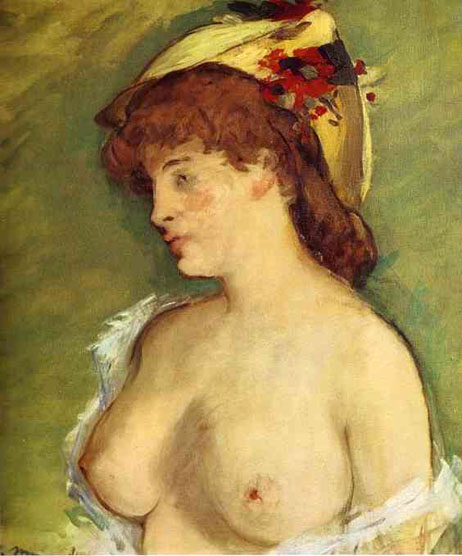
Manet embarked on the canvas after being challenged to give the Salon a nude painting to display. The painting was controversial partly because the nude is wearing some small items of clothing such as an orchid in her hair, a bracelet, a ribbon around her neck, and mule slippers, all of which accentuated her nakedness, comfortable courtesan lifestyle and sexuality. The orchid, upswept hair, black cat, and bouquet of flowers were all recognized symbols of sexuality at the time. This modern Venus' body is thin, counter to prevailing standards; the painting's lack of idealism rankled viewers who noticed it despite its placement, high on the wall of the Salon. A fully-dressed black servant is featured, exploiting the then-current theory that black people were hyper-sexed. That she is wearing the clothing of a servant to a courtesan here, furthers the sexual tension of the piece.
The flatness of Olympia is inspired by Japanese wood block art. Her flatness serves to make her more human and less voluptuous. Her body as well as her gaze is unabashedly confrontational. She defiantly looks out as her servant offers flowers from one of her male suitors. Although her hand rests on her leg, hiding her pubic area in a "frog" gesture - also another sex symbol, the reference to traditional female virtue is ironic; a notion of modesty is notoriously absent in this work. The alert black cat at the foot of the bed strikes a sexually rebellious note in contrast to that of the sleeping dog in Titian's portrayal of the goddess in his Venus of Urbino. Manet's uniquely frank (and largely unpopular) depiction of a self-assured prostitute was accepted by the Paris Salon in 1865. At the same time, his notoriety translated to popularity in the French avant-garde community.
"Olympia" immediately launched responses. Caricatures, sketches, and paintings, all addressed this nude. Artists such as Pablo Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Gustave Courbet, Paul Cézanne, and Claude Monet all appreciated the painting's significance.
As with Luncheon on the Grass, the painting raised the issue of prostitution within contemporary France and the roles of women within society.
The roughly painted style and photographic lighting in these works was seen as specifically modern, and as a challenge to the Renaissance works Manet copied or used as source material. His work is considered 'early modern', partially because of the black outlining of figures, which draws attention to the surface of the picture plane and the material quality of paint.
He became friends with the Impressionists Edgar Degas, Claude Monet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, Alfred Sisley, Paul Cézanne, and Camille Pissarro, through another painter, Berthe Morisot, who was a member of the group and drew him into their activities. The grand niece of the painter Jean-Honoré Fragonard, Morisot's paintings first had been accepted in the Salon de Paris in 1864 and she continued to show in the salon for ten years.

Manet became the friend and colleague of Berthe Morisot in 1868. She is credited with convincing Manet to attempt plein air painting, which she had been practicing since she had been introduced to it by another friend of hers, Camille Corot. They had a reciprocating relationship and Manet incorporated some of her techniques into his paintings. In 1874, she became his sister-in-law when she married his brother, Eugene.

_1869_70.jpg)
Unlike the core Impressionist group, Manet maintained that modern artists should seek to exhibit at the Paris Salon rather than abandon it in favor of independent exhibitions. Nevertheless, when Manet was excluded from the International exhibition of 1867, he set up his own exhibition. His mother worried that he would waste all his inheritance on this project, which was enormously expensive. While the exhibition earned poor reviews from the major critics, it also provided his first contacts with several future Impressionist painters, including Degas.
Although his own work influenced and anticipated the Impressionist style, he resisted involvement in Impressionist exhibitions, partly because he did not wish to be seen as the representative of a group identity, and partly because he preferred to exhibit at the Salon. Eva Gonzalès was his only formal student.
He was influenced by the Impressionists, especially Monet and Morisot. Their influence is seen in Manet's use of lighter colors, but he retained his distinctive use of black, uncharacteristic of Impressionist painting. He painted many outdoor (plein air) pieces, but always returned to what he considered the serious work of the studio.


Manet enjoyed a close friendship with composer Emmanuel Chabrier, painting two portraits of him; the musician owned 14 of Manet's paintings and dedicated his Impromptu to Manet's wife.
Throughout his life, although resisted by art critics, Manet could number as his champions Émile Zola, who supported him publicly in the press, Stéphane Mallarmé, and Charles Baudelaire, who challenged him to depict life as it was. Manet, in turn, drew or painted each of them.


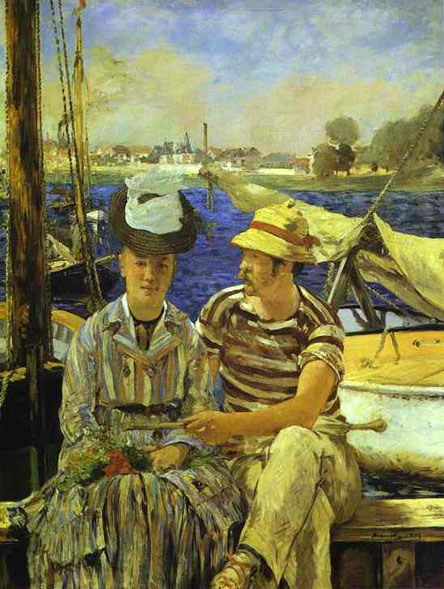
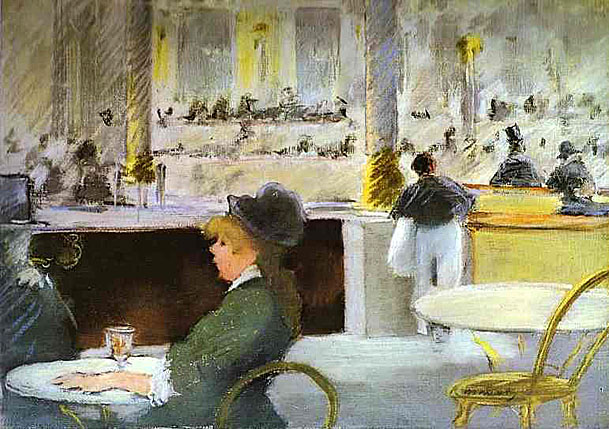
Manet's paintings of cafe scenes are observations of social life in nineteenth century Paris. People are depicted drinking beer, listening to music, flirting, reading, or waiting. Many of these paintings were based on sketches executed on the spot. He often visited the Brasserie Reichshoffen on boulevard de Rochechourt, upon which he based At the Café in 1878. Several people are at the bar, and one woman confronts the viewer while others wait to be served. Such depictions represent the painted journal of a flâneur. These are painted in a style which is loose, referencing Hals and Velázquez, yet they capture the mood and feeling of Parisian night life. They are painted snapshots of bohemianism, urban working people, as well as some of the bourgeoisie.

In Corner of a Cafe Concert, a man smokes while behind him a waitress serves drinks. In The Beer Drinkers a woman enjoys her beer in the company of a friend. In The Cafe Concert a sophisticated gentleman sits at a bar while a waitress stands resolutely in the background, sipping her drink. In The Waitress, a serving woman pauses for a moment behind a seated customer smoking a pipe, while a ballet dancer, with arms extended as she is about to turn, is on stage in the background.


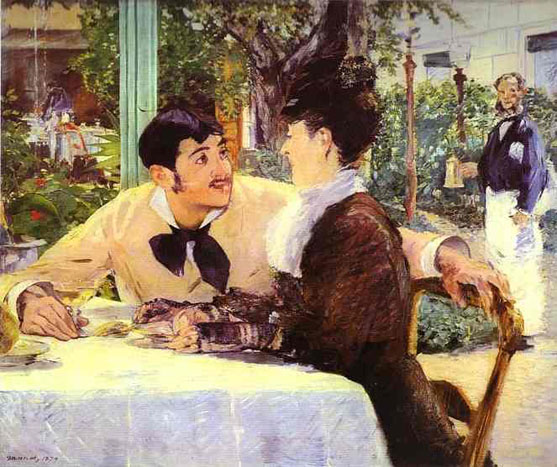
Manet also sat at the restaurant on the Avenue de Clichy called Pere Lathuille's, which had a garden as well as the dining area. One of the paintings he produced here was, At Pere Lathuille's, in which a man displays an unrequited interest in a woman dining near him.
In Le Bon Bock, a large, cheerful, bearded man sits with a pipe in one hand and a glass of beer in the other, looking straight at the viewer.

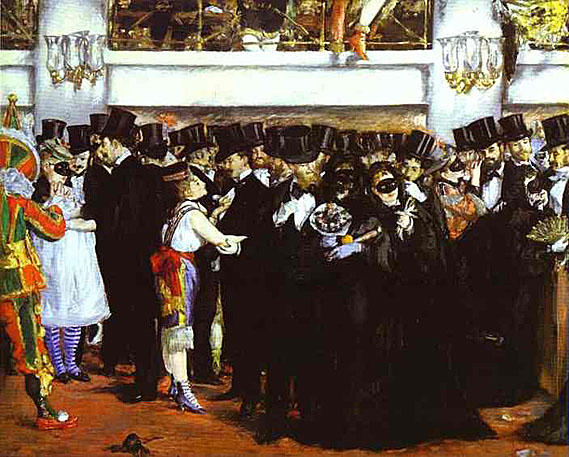
Manet also painted the upper class enjoying more formal social activities. In Masked Ball at the Opera, Manet shows a lively crowd of people enjoying a party. Men stand with top hats and long black suits while talking to women with masks and costumes. He included portraits of his friends in this picture.

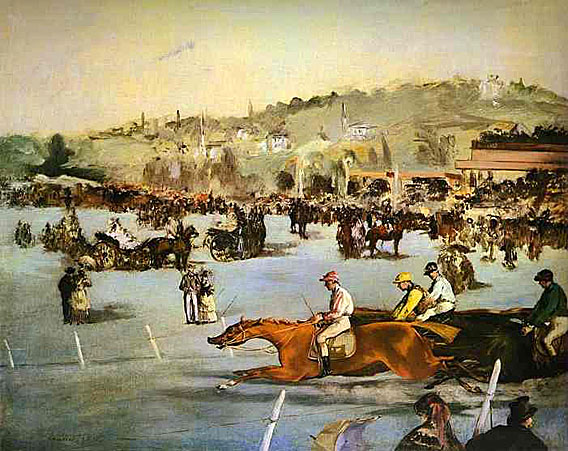
Manet depicted other popular activities in his work. In Racing at Longchamp, an unusual perspective is employed to underscore the furious energy of racehorses as they rush toward the viewer. In Skating Manet shows a well dressed woman in the foreground, while others skate behind her. Always there is the sense of active urban life continuing behind the subject, extending outside the frame of the canvas.

In View of the International Exhibition, soldiers relax, seated and standing, prosperous couples are talking. There is a gardener, a boy with a dog, a woman on horseback - in short, a sample of the classes and ages of the people of Paris.
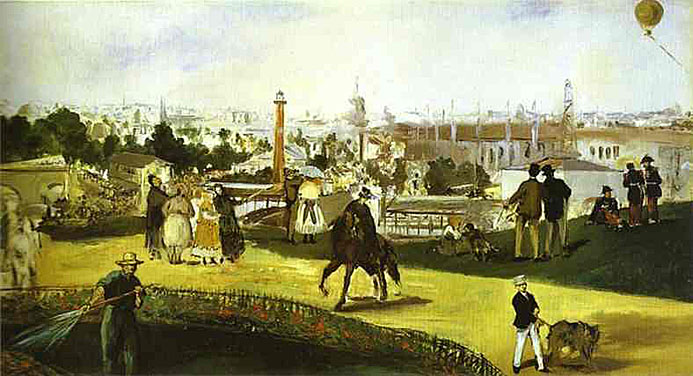
Manet's response to modern life included works devoted to war, in subjects that may be seen as updated interpretations of the genre of "history painting". The first such work was the Battle of the Kearsarge and Alabama (1864), a sea skirmish from the American Civil War which took place off the French coast, and may have been witnessed by the artist.

Of interest next was the French intervention in Mexico; from 1867 to 1869 Manet painted three versions of the Execution of Emperor Maximilian, an event which raised concerns regarding French foreign and domestic policy. The several versions of the Execution are among Manet's largest paintings, which suggest that the theme was one which the painter regarded as most important. Its subject is the execution by Mexican firing squad of a Hapsburg emperor, who had been installed by Napoleon III. Neither the paintings nor a lithograph of the subject were permitted to be shown in France. As an indictment of formalized slaughter the paintings look back to Goya, and anticipate Picasso's Guernica.
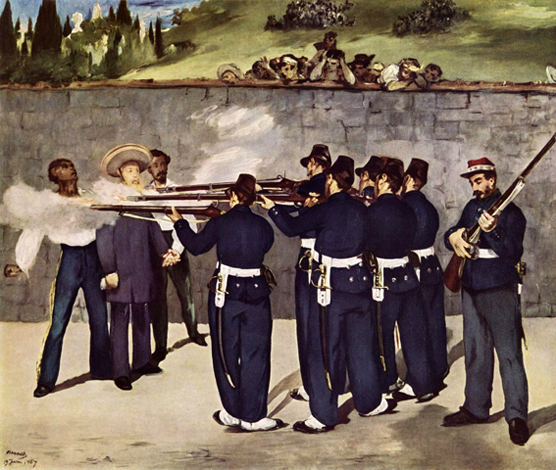
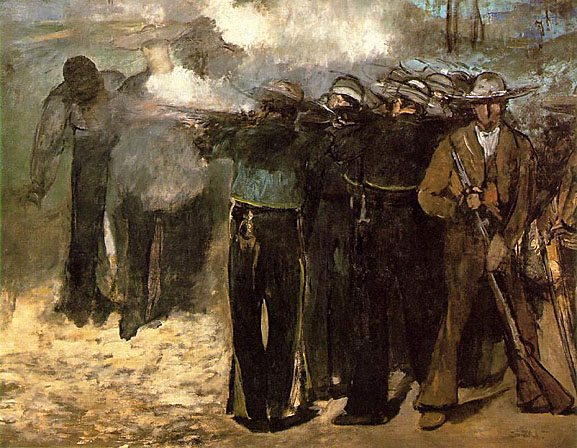


In January 1871 Manet traveled to Oloron-Sainte-Marie in the Pyrenees. In his absence his friends added his name to the "Fédération des artistes" of the Paris Commune. Manet stayed away from Paris, perhaps, until after the semaine sanglante. In a letter to Berthe Morisot at Cherbourg (June 10, 1871) he writes: "We came back to Paris a few days ago...".
The Prints and Drawings Collection of the Museum of Fine Arts (Budapest) has a watercolor/gouache (The Barricade) by Manet depicting a summary execution of Communards by Versailles troops based on a lithograph of the execution of Maximilian. A similar piece (The Barricade), oil on plywood, is held by a private collector.
.jpg)
On 18 March 1871 he wrote to his (confederate) friend Félix Bracquemond in Paris about his visit to Bordeaux, the provisory seat of the French National Assembly of the Third French Republic where Emile Zola introduced him to the sites: "I never imagined that France could be represented by such doddering old fools, not excepting that little twit Thiers..." If this could be interpreted as support of the Commune a following letter to Bracquemond (March 21, 1871) expressed his idea more clearly: "Only party hacks and the ambitious, the Henrys of this world following on the heels of the Milliéres, the grotesque imitators of the Commune of 1793..." He knew the communard Lucien Henry to have been a former painter's model and Millière, an insurance agent. "What an encouragement all these bloodthirsty caperings are for the arts! But there is at least one consolation in our misfortunes: that we're not politicians and have no desire to be elected as deputies".
Manet depicted many scenes of the streets of Paris in his works. The Rue Mosnier Decked with Flags depicts red, white, and blue pennants covering buildings on either side of the street--another painting of the same title features a one-legged man walking with crutches. Again depicting the same street, but this time in a different context, is Rue Monsnier with Pavers, in which men repair the roadway while people and horses move past.

The Railway, widely known as The Gare Saint-Lazare, was painted in 1873. The setting is the urban landscape of Paris in the late nineteenth century. Using his favorite model in his last painting of her, a fellow painter, Victorine Meurent, also the model for Olympia and the Luncheon on the Grass, sits before an iron fence holding a sleeping puppy and an open book in her lap. Next to her is a little girl with her back to the painter, who watches a train pass beneath them.
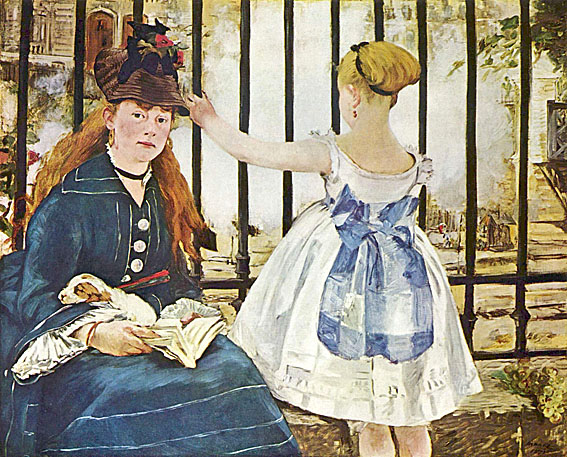
Instead of choosing the traditional natural view as background for an outdoor scene, Manet opts for the iron grating which "boldly stretches across the canvas". The only evidence of the train is its white cloud of steam. In the distance, modern apartment buildings are seen. This arrangement compresses the foreground into a narrow focus. The traditional convention of deep space is ignored.
When the painting was first exhibited at the official Paris Salon of 1874: "Visitors and critics found its subject baffling, its composition incoherent, and its execution sketchy. Caricaturists ridiculed Manet's picture, in which only a few recognized the symbol of modernity that it has become today".
He completed painting his last major work, A Bar at the Folies-Bergère (Le Bar aux Folies-Bergère), in 1882 and it hung in the Salon that year.
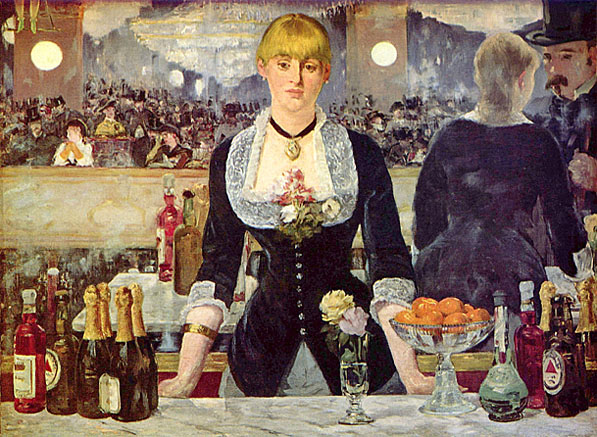
In 1875, a French edition of Edgar Allan Poe's The Raven included lithographs by Manet and translation by Mallarmé.
In 1881, with pressure from his friend Antonin Proust, the French government awarded Manet the Légion d'honneur.
In 1863 Manet married Suzanne Leenhoff, a Dutch-born piano teacher of his own age with whom he had been romantically involved for approximately ten years. Leenhoff initially had been employed by Manet's father, Auguste, to teach Manet and his younger brother piano. She also may have been Auguste's mistress. In 1852, Leenhoff gave birth, out of wedlock, to a son, Leon Koella Leenhoff.
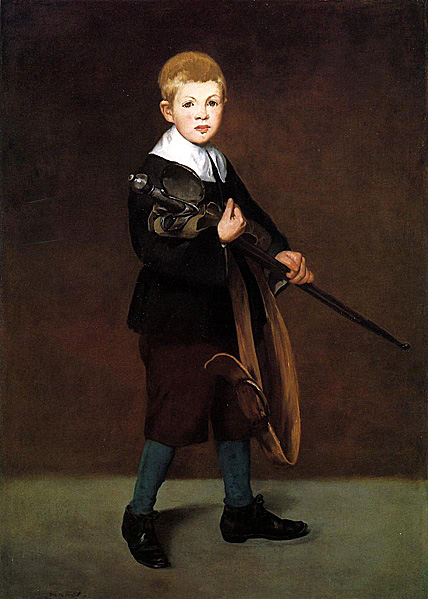
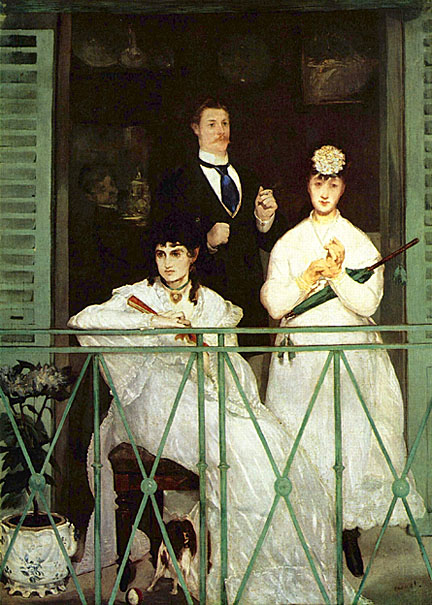
After the death of his father in 1862, Manet married Suzanne. Eleven-year-old Leon Leenhoff, whose father may have been either of the Manets, posed often for Manet. Most famously, he is the subject of the Boy Carrying a Sword of 1861. He also appears as the boy carrying a tray in the background of The Balcony.

Manet died of untreated syphilis and rheumatism, which he contracted in his forties. The disease caused him considerable pain and partial paralysis from locomotor ataxia in the years prior to his death.
His left foot was amputated because of gangrene; an operation followed eleven days later by his death. He died at the age of fifty-one in Paris in 1883, and is buried in the Cimetière de Passy in the city.






_1881.jpg)
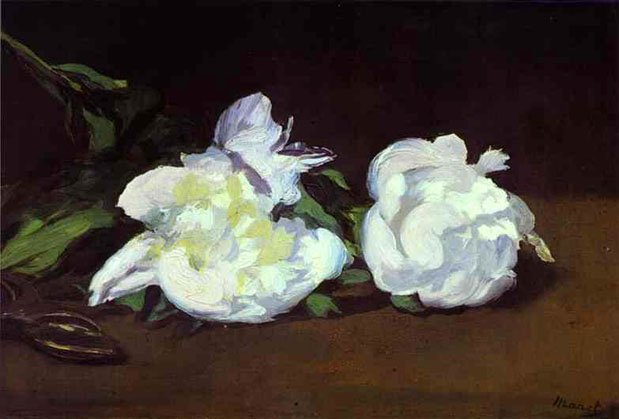




This is what Manet does so effectively in his Peonies with the spontaneity and directness of brushwork that was always at his command. The form of the flower is no more than suggested but its splendor as a receptacle of light is fully conveyed by the seemingly simple division of color tones.

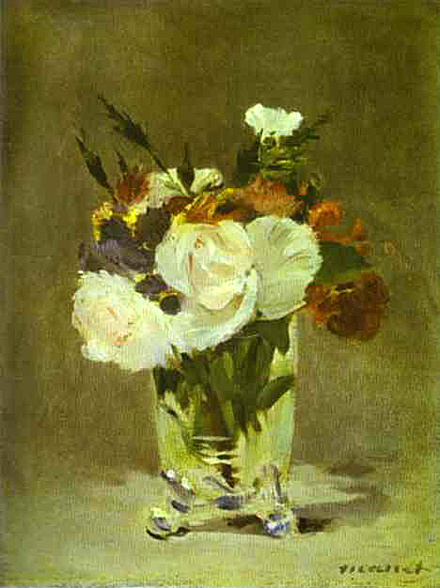

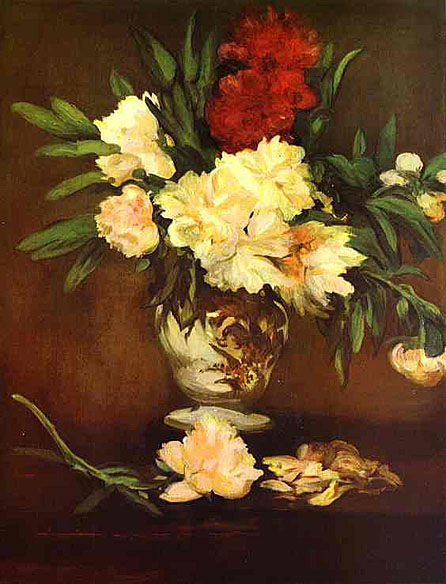



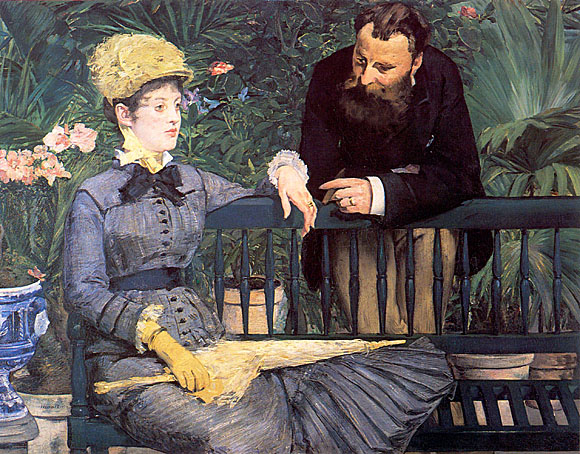
_1868.jpg)
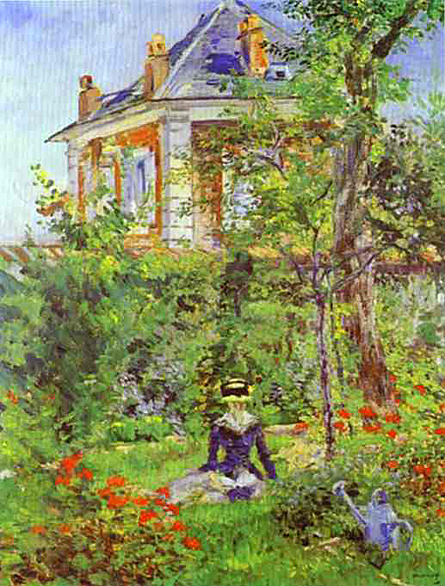





Despite these handicaps, he wished his time there to be productive and in those letters he complained that bad weather restricted his painting activity, particularly out of doors. However, this painting and others from the same time do not reflect emotional or physical disparity.
The size of the canvas is comparatively large, implying that his ambition and means to execute substantial work had not diminished. It is also signed and dated, indicating that he considered the work finished. The paint is handled with astonishing exuberance and energy, especially in the grassy clumps beneath the tree, in the foliage and in the curving pathway. The light is shimmering and bright and the view is charged with vitality and life.
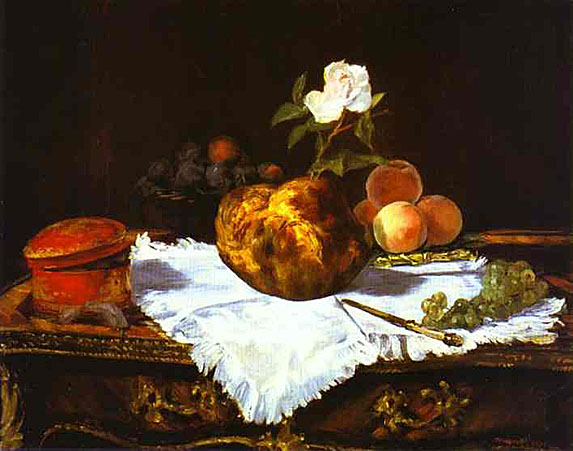



_1878_79.jpg)
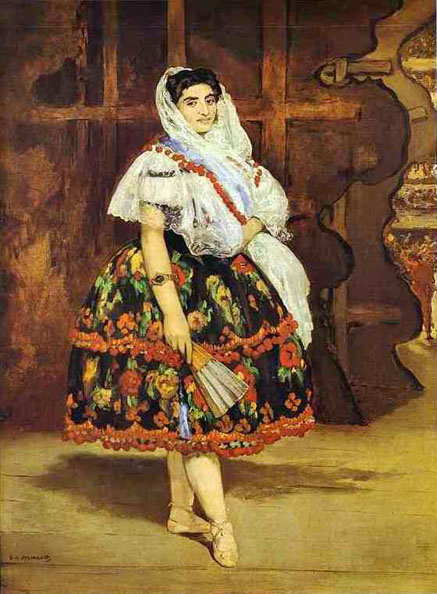
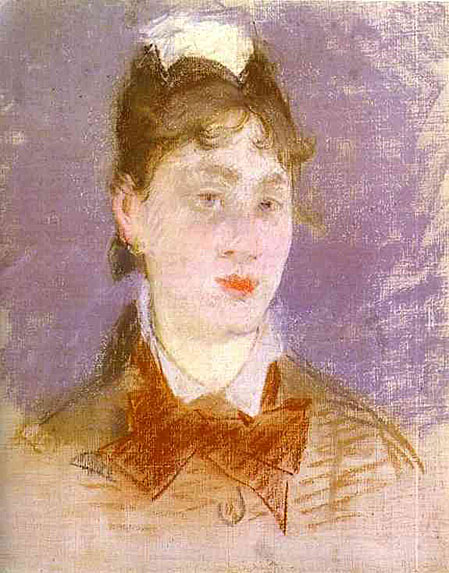


_1878.jpg)
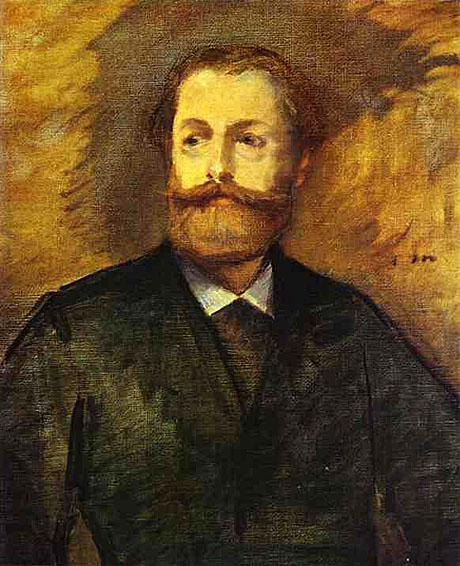










Antonin Proust was born at Niort. In 1864 he founded an anti-imperial journal, La Semaine hebdomadaire which appeared in Brussels. He was war correspondent for Le Temps in the early days of the Franco-German War, but after Sedan he returned to Paris, where he became secretary to Gambetta and superintended the refugees in Paris. He entered the Chamber as deputy for his native town in 1876, taking his seat on the left. In Gambetta's cabinet (1881-1882) he was minister of the fine arts, and in the Chamber of Deputies he was regularly commissioned to draw up the budget for the fine arts, after the separate department had ceased to exist. Prosecuted in connection with the Panama scandals, he was acquitted in 1893. From this time he lived in the closest retirement. On the 20th of March 1905 he shot himself in the head, dying of the wound two days later.

As a naturalistic writer, he was amongst the first English-language authors to absorb the lessons of the French realists, and was particularly influenced by the works of Émile Zola. His writings influenced James Joyce, according to the literary critic and biographer Richard Ellmann, and, although Moore's work is sometimes seen as outside the mainstream of both Irish and British literature, he is as often regarded as the first great modern Irish novelist.
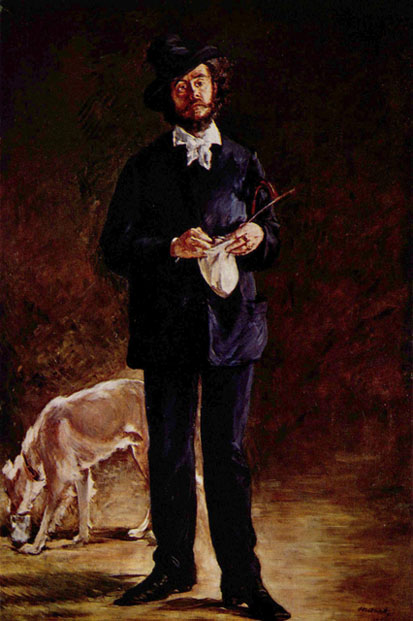

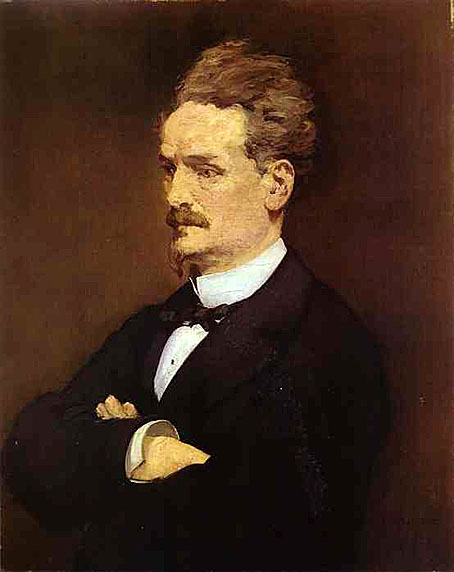
His father was a Legitimist noble who as Édmond Rochefort was well known as a writer of vaudevilles; his mother's views were republican. After experience as a medical student, a clerk at the Hôtel de Ville, a playwright and a journalist, he joined the staff of Le Figaro in 1863; but a series of his articles, afterwards published as Les Français de la Décadence brought the paper into collision with the authorities and caused the termination of his engagement.
In collaboration with different dramatists he had meanwhile written a long series of successful vaudevilles, which began with the Monsieur bien mis at the Folies Dramatiques in 1856. On leaving Le Figaro Rochefort determined to start a paper of his own, La Lanterne. The paper was seized on its eleventh appearance, and in August 1868 Rochefort was fined 10,000 francs, with a year's imprisonment.
He then published his paper in Brussels, from where it was smuggled into France. Printed in French, English, Spanish, Italian and German, it went the round of Europe. After a second prosecution he fled to Belgium. A series of duels, of which the most famous was one fought with Paul de Cassagnac a propos of an article on Joan of Arc, kept Rochefort in the public eye.
In 1869, after two unsuccessful candidatures, he was returned to the Chamber of Deputies by the first circumscription of Paris. He was arrested on the frontier, only to be almost immediately released, and forthwith took his seat.
He renewed his onslaught on the empire, starting a new paper, La Marseillaise, as the organ of political meetings arranged by himself at La Villette. The staff was appointed on the votes of the members, and included Victor Noir and Paschal Grousset. The violent articles in this paper led to the duel which resulted in Victor Noir's death at the hands of Prince Pierre Bonaparte. The paper was seized, and Rochefort and Grousset were sent to prison for six months.
The revolution of September was the signal for his release. He became a member of the Government of National Defense, but this short association with the forces of law and order was soon broken on account of his openly expressed sympathy with the Communards. On May 11 1871 he fled in disguise from Paris. A week earlier he had resigned with a handful of other deputies from the National Assembly rather than countenance the dismemberment of France. Arrested at Meaux by the Versailles government, he was detained for some time in prison with a nervous illness before he was condemned under military law to imprisonment for life.
In spite of Victor Hugo's efforts on his behalf he was transported to New Caledonia. In 1874 he escaped on board an American vessel to San Francisco. He lived in London and Geneva until the general amnesty permitted his return to France in 1880. In Geneva he resumed the publication of La Lanterne, and in the Parisian papers articles constantly appeared from his pen.
When at length in 1880 the general amnesty permitted his return to Paris he founded L'Intransigeant in the Radical and Socialist interest. For a short time in 1885-86 he sat in the Chamber of Deputies, but found a great opportunity next year for his talent for inflaming public opinion in the Boulangist agitation. He was condemned to detention in a fortress in August 1889 at the same time as General Boulanger, whom he had followed into exile. He continued his polemic from London, and after the suicide of General Boulanger he attacked M. Constans, minister of the interior in the Freycinet cabinet, with the utmost violence, in a series of articles which led to an interpellation in the chamber in circumstances of wild excitement and disorder.
The Panama scandals furnished him with another occasion, and he created something of a sensation by a statement in Le Figaro that he had met M. Clemenceau at the table of the financier Cornelius Herz. In 1895 he returned to Paris, two years before the Dreyfus affair supplied him with another point d'appui. He became prominent among the anti-Dreyfusards, and had a principal share in the organization of the press campaign. Subsequently he was editor of La Patrie. As a result of his journalistic descent, this aristocratic scribe is remembered today as "the prince of the gutter press" ("le Prince des polémistes").


Manet was entranced by Isabelle, sending her, during his summer stay at Bellevue in 1880, a sequence of charming, witty flirtatious letters often accompanied by watercolor sketches. She rarely, if ever replied and was equally cavalier about her portraits.
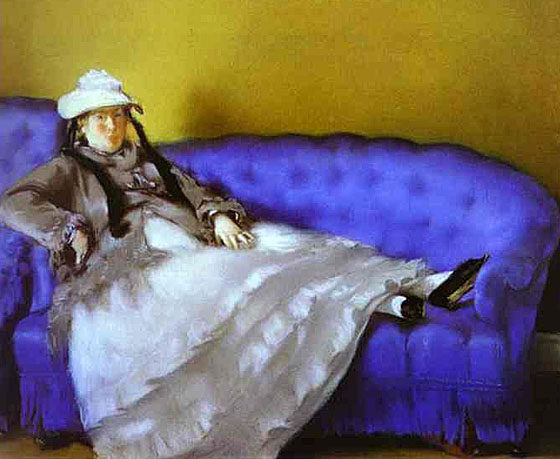
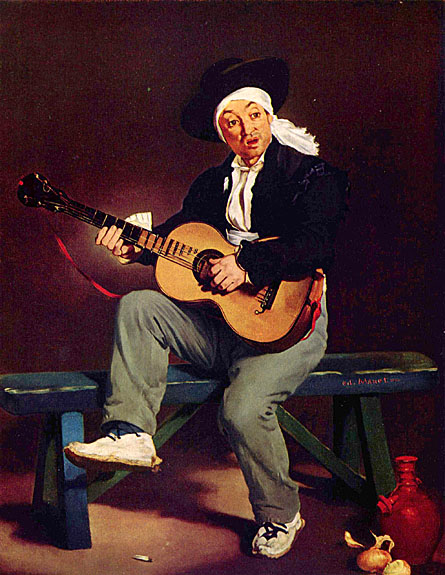
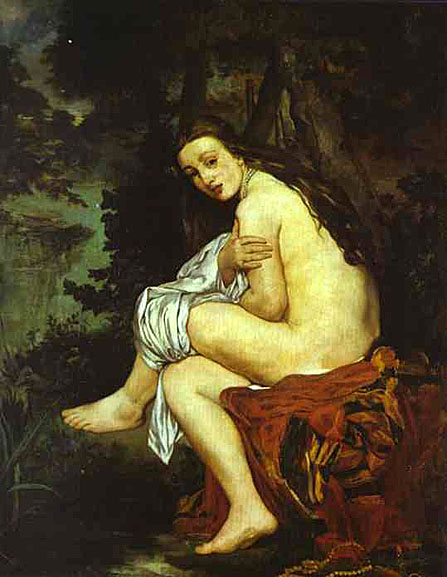
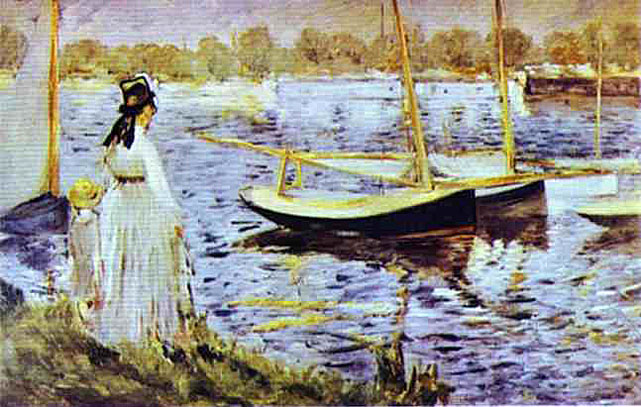
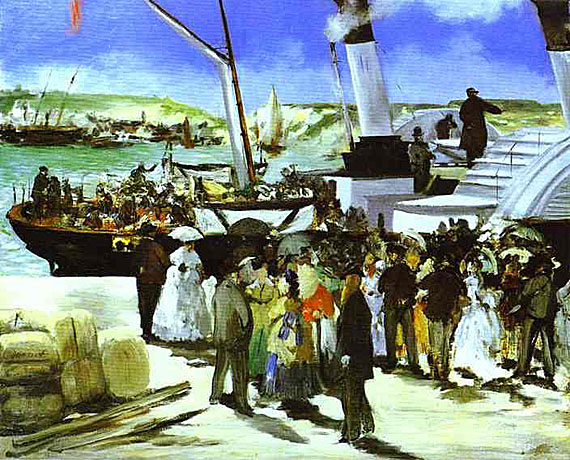
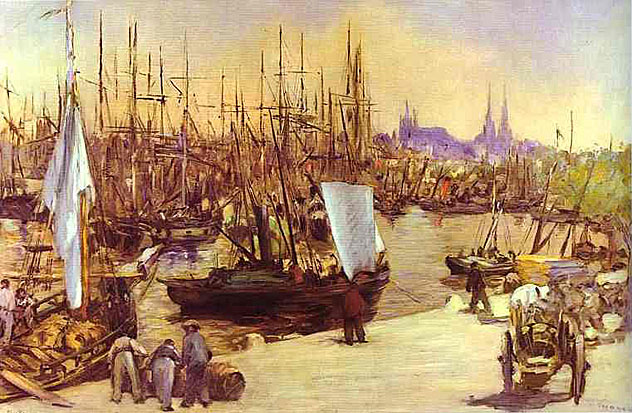
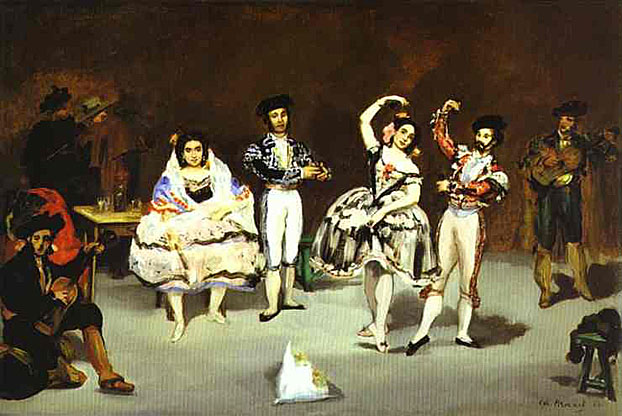





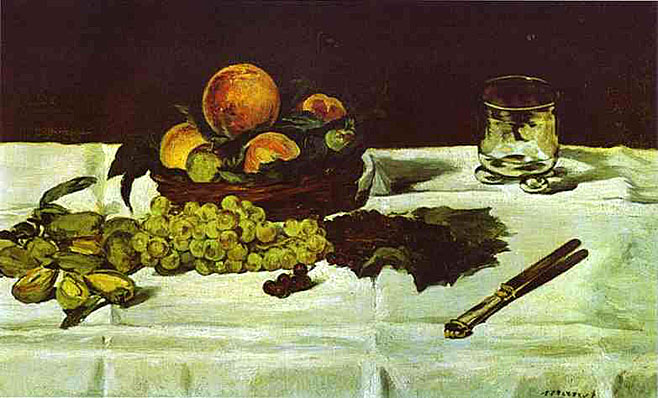







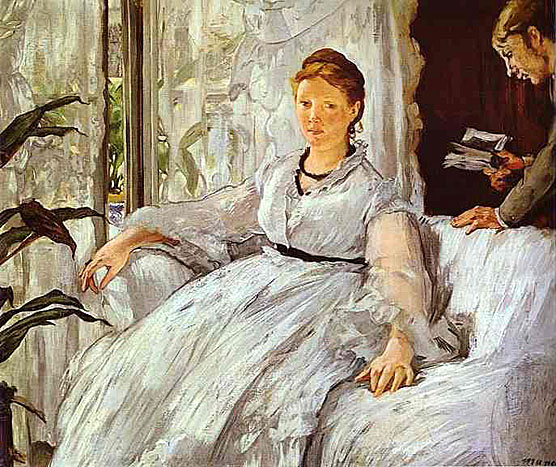


_1865_66.jpg)
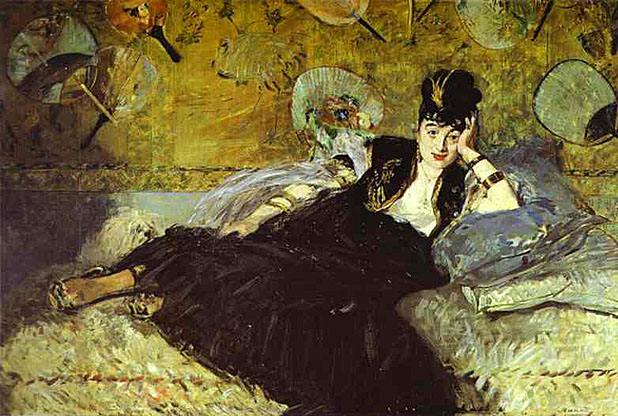
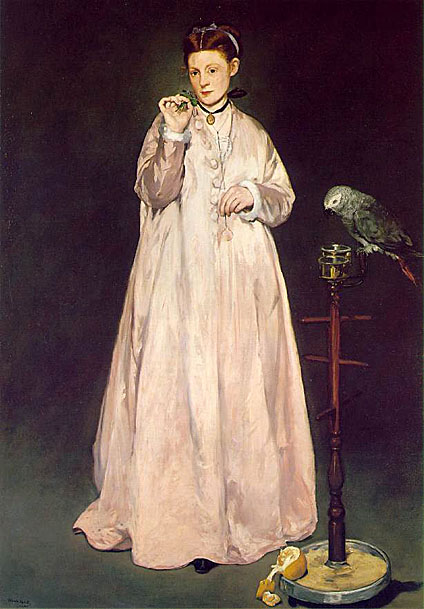
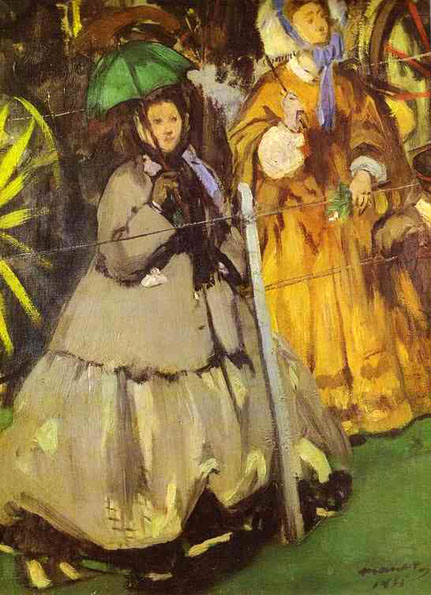





Source: Art Renewal Center
Source: Web Museum
Return to Pagina Artis
Return to Bruce and Bobbie's Main Page.